Cyber Vault
A-to-Zerto Glossary of Terms
Overview
Cyber Vaults represent the pinnacle of secure storage solutions, designed to safeguard critical data and application against cyber threats and data loss. They often act as a last line of defense. Beyond mere data storage, cyber vaults play a pivotal role in cyber resilience by ensuring rapid incident response and recovery efforts.
Related Topics
What Is a Cyber Vault?
A cyber vault is a highly secure repository designed to safeguard critical data and applications against cyber threats. Employing a multi-layered defense strategy, cyber vaults utilize advanced encryption, access controls, and monitoring mechanisms to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, ransomware, and data loss.
These vaults serve as a last resort for businesses to recover their data and restore operations in the event of a cyberattack or system failure, mitigating the risk of data loss. By centralizing data within an immutable backup, using a cyber vault ensures that critical information remains intact and accessible, even in the worst-case scenarios.
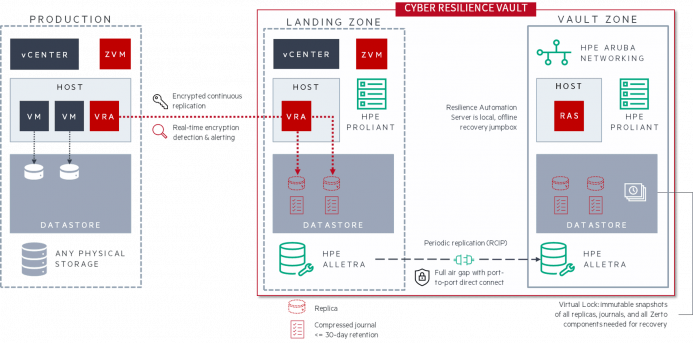
Example of a cyber vault architecture: Zerto Cyber Resilience Vault.
Why You Need a Cyber Vault to Improve Cyber Resilience
Cyber vaults offer several key benefits that are essential for improving cyber resilience in today’s dynamic landscape. Firstly, they provide an ironclad infrastructure for critical data and applications, offering secure refuge against cyber threats such as ransomware and data breaches.
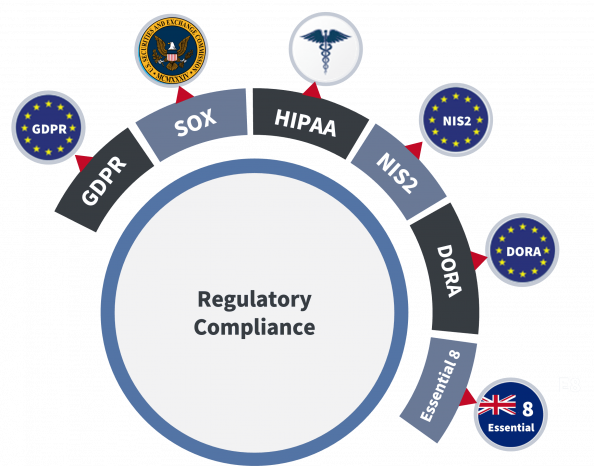
Moreover, cyber vaults are vital in helping organizations meet compliance and regulatory requirements. With data protection regulations becoming increasingly stringent, such as GDPR, HIPAA, DORA, NIS2, and SOX, businesses must ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data. Cyber vaults serve as a key compliance enabler by providing a secure environment for storing and managing sensitive data, facilitating audits, and demonstrating adherence to regulatory mandates.
Comparing Resilience – Part Four: Cyber Resilience
What is Cyber Resilience
What Is the Difference between a Cyber Vault and an Immutable Data Vault?
As its name implies, an immutable data vault keeps immutable copies of the most critical data an organization generates and holds. It uses some type of air gap to isolate and safeguard the data against cyber threats.
A cyber vault, on top of including an immutable data vault, also provide an isolated recovery environment dedicated to the recovery operations. It is not just about having access to reliable copies of an organization's critical data. It is about being able to leverage these immutable backups to orchestrate and automate a quick recovery in an isolated and clean environment.
Both types of vaults most likely leverage some type of ransomware and malware detection to ensure that the data being copied is not compromised in any way.
Types of Immutable Data Vaults
Ransomware Detection Part 1: What Is Ransomware Detection?
What Makes a True Cyber Vault Superior to an Immutable Data Vault?
The cyber vault's integration of purpose-built isolation and immutable data storage, alongside its orchestration and automation features for recovery, streamlines management and enhances recovery speed while minimizing downtime. With reduced reliance on external network connections for management, air-gapping becomes more robust.
Since a cyber vault requires software, compute, storage and networking components , it is often better to use a solution from one vendor as to ensure a tight and neat integration between all these components. This also often results in a more comprehensive and unified technical support to manage and maintain the solution, alongside a lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
In contrast, an immutable data vault, while also protecting and maintaining the integrity of the data, can help with the recovery, but it cannot be the engine driving the recovery. Remember, if your production environment has been fully compromised, having access to the data to recover is useless if you don't have the infrastructure to run the data and applications needed to resume your operations.
The Importance of Isolated Recovery Environments and Immutable Cyber Data Vaults
Backup Is Most Definitely NOT Disaster Recovery
Cyber Vault and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Cyber vaults serve as essential components in meeting various cybersecurity standards, such as NIST. These secure infrastructures provide robust protection mechanisms by employing encryption, access controls, and other security measures to safeguard critical data and applications.
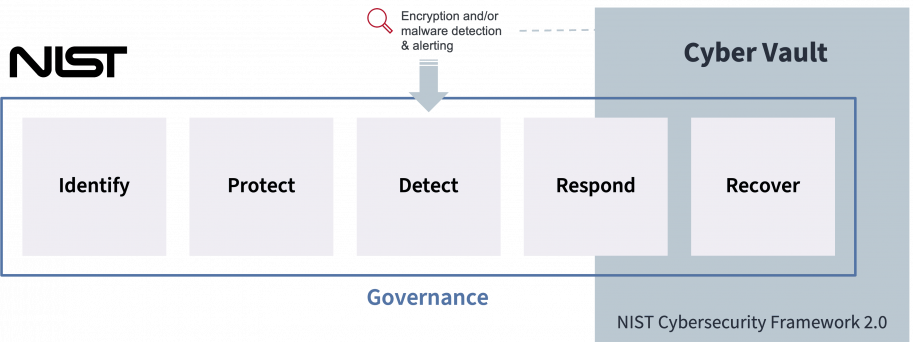
Additionally, modern cyber vault environments should include detection capabilities, enabling early identification of cyber-threats. By monitoring for anomalies and suspicious activities, organizations can respond swiftly, limiting the propagation of attacks and minimizing potential damage.
Finally, cyber vaults play a crucial role in recovery efforts by maintaining resilient backup infrastructure and immutable backups. This ensures quick restoration of operations, minimizing downtime, maintaining business continuity, and improving cyber resilience, even in the face of cyber incidents.
Managing Cyberthreats to Combat Ransomware Part 3: Cybersecurity Frameworks
Why Real-Time Encryption Detection Matters
Cyber Vault and the 3-2-1 Rule
The 3-2-1 rule can be broken down into three simple parts:
- Keep 3 copies of data, including all production data and two backup copies.
- Store backup copies on 2 different types of storage, including any combination of on-premises, cloud, or offline options.
- Ensure 1 backup copy is stored at an off-site location, such as a public cloud server.
While still a foundational rule, the cyber-threat landscape continues to evolve and additional measures are necessary to fortify backup strategies.
By incorporating an air gap, which requires at least one copy of the data to be stored offline and inaccessible, organizations can enhance protection against ransomware attacks that target online and network-connected backups.
Cyber vaults serve as an integral component of implementing this strategy, providing a secure and isolated environment for storing critical data offline.
Furthermore, access management based on a zero-trust framework adds an extra layer of security, ensuring that only authorized individuals or systems can access the cyber vault.
By adhering to the 3-2-1 rule and incorporating air gap strategies within cyber vaults, organizations can significantly improve their cyber resilience.
What Is An Air Gap in Data Protection
The 3-2-1 Backup Rule
What to Look for in a True Cyber Vault?
Ransomware threats and cyberattacks continue to growing in frequency, severity, and sophistication. When looking for a cyber vault that protects against ransomware attacks and builds cyber resilience it’s important to take in account the following features:
Recovery Capabilities
- Compute, storage, and networking to temporarily run virtualized infrastructure in isolated environment
- Production-grade storage designed for mission-critical workloads
- Integrated orchestration and automation capabilities
- Cross-VM (virtual machine) consistency to support multi-VM applications
- Frequent immutable copies available for recovery
Air-Gapping Quality
- Type of air gap: physical, logical, or both (best)
- Number of connections to outside networks required kept to a minimum
- Security protocol and methods to access the vault
Use of Decentralized Zero Trust Architectures
- Fully encrypted traffic between all components
- Identity and access control (credentials protection, least-privilege access, etc.)
- Decentralized control plane
Security Scanning Methods and Capabilities for Detection
- Type of scanning: real-time detection (best), periodic
- Scanning location: inline during replication (as the data streams) or on a backup appliance (usually throttles scanning speed)
- Abilities to integrate security scanning into security information and event management (SIEM) systems, or security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) solutions, to improve overall threat detection by security teams
Reliability and Advancement of Technologies Involved
- Replication type: synchronous, near-synchronous, asynchronous
- Replication technology: hypervisor-based, storage-based, appliance-based
- Hardware hardening features (FIPS-validated hardware, Linux appliances, tamper-proof NTP protection, silicon root of trust,etc.)
- Networking features
- Encryption at rest and in flight
Zerto’s Cyber Resilience Vault: Rapid Air-Gapped Recovery
The Zerto Cyber Resilience Vault by Zerto, a Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company, is a purpose-built isolated recovery environment and immutable data vault combined into a single solution.
It’s expertly designed upon production-grade storage, compute, and networking to help organizations unlock rapid air-gapped recovery from even the worst and widespread cyberattacks.
By using the only dedicated cyber recovery solution on the market to utilize continuous data protection, organizations can see potential reductions in RTOs and RPOs against other cyber recovery vault solutions in the market.
Zerto Cyber Resilience Vault
Why Zerto Cyber Resilience Vault
Other Resources
LATEST FROM ZERTO SEE ALL
Cyber Vaults
Check the available Zerto resources about cyber vaults.
Building a Cyber Resilience Vault with Zerto
Learn about Zerto’s vault architecture, combining Zerto’s ultra-low RPOs and RTOs with the untouchable performance of HPE hardware, and enabling you to architect and customize an ironclad recovery vault.
Essential Guide: Ransomware Recovery
From the definition of ransomware, description of how a ransomware attack unfolds, right down to cyber resilience and ransomware recovery, we cover everything in this ultimate guide.
What is Zerto?
Learn about Zerto and how it can help you solve your data protection and recovery challenges.