Risk Management
A-to-Zerto Glossary of Terms
Overview
Risk management is the process that an organization implements to prevent disruptive events, or longer-term trends that can have a negative impact. It covers strategic, financial, operational, and compliance and governance risks. The goal of risk management for operational risks is true business continuity with always-on availability.
Related Topics
What Is Risk Management ?
Risk management is the activity of identifying, analyzing, and responding to threats and risk factors that impact an organization's profitability, viability, and strategic goals. These threats are multi-varied and include emergencies, natural disasters, IT or technological issues, legal or regulatory problems, and financial uncertainties. Risk management attempts to control future threats by planning preemptively and deploying effective risk-control measures.
For IT infrastructure and operations, organizations achieve risk management through business continuity and disaster recovery.
What Is the Risk Management Process?
The risk management process identifies, assesses, and monitors risks on an ongoing basis. It highlights risks that are outside of the organization's risk appetite —risks that cross over the threshold of what it can tolerate— and implements controls to mitigate the occurrence and impact of these risks.
Risk management covers strategic, financial, operational, and compliance and governance risks. Although the approach to each of these areas is similar, it can differ due to the specifics of each area. So while the risk management process for financial risks may have elements not found in the process for compliance and governance risk, they will both cover assessment, alignment and investment decisions over mitigation.
Figure 1 illustrates what the risk management process may look like for managing operational risks, with its two specific elements: business continuity and disaster recovery.
Figure 1: Risk management process for operational risks
The leadership team is a key element in this process and is responsible for defining the risk appetite in each area to align with and support the organization's business strategy.
Therefore, teams managing these risks can determine which controls or actions are needed to eliminate or reduce any residual risk within the organization's risk tolerance. They can also identify new risks arising from changes to the environment or the business strategy. Leadership can then prioritize these risks and can invest in recommended controls.
What is Risk Assessment?
What is Business Impact Analysis?
How Is Risk Management Related to Business Strategy?
The importance of risk management in business strategy cannot be overstated. Risk management views weaknesses, threats, and operational blind spots as negative risks, but sees opportunities as positive risks. Within the context of business strategy, risk management enables business leaders to implement measured responses to bolster areas of weakness while mitigating or avoiding the impact of threats.
Risk management is intrinsic to the effective implementation of business strategy, but it also gets shaped by it through the definition of an organization's risk appetite.
Besides focusing on internal and external threats, risk management also considers how to manage positive risk — taking advantage of opportunities that could help the organization achieve its business goal and gain an edge over the competition.
What is the Relationship between Risk Management and Business Resilience?
In today's world, business resilience is an increasingly important prerequisite for competitive corporate performance. Recent crises have demonstrated that economies and industries are vulnerabilities to supply chain disruptions and demand shocks. Organizations are also subject to disruptive currents such as inflation, price volatility, cyber threats, and accelerating digitization.
The nature of change —both dynamic and evolving— makes it difficult to predict disruptions even as they grow in frequency and severity. To stay ahead of such disruptions, organizations need to build up their response capabilities in advance. This is where risk management steps in.
The aim is to transition away from a reactive (crisis response) mode and integrate enterprise risk management into business strategy, operations, and organizational culture creating true business resiliency.
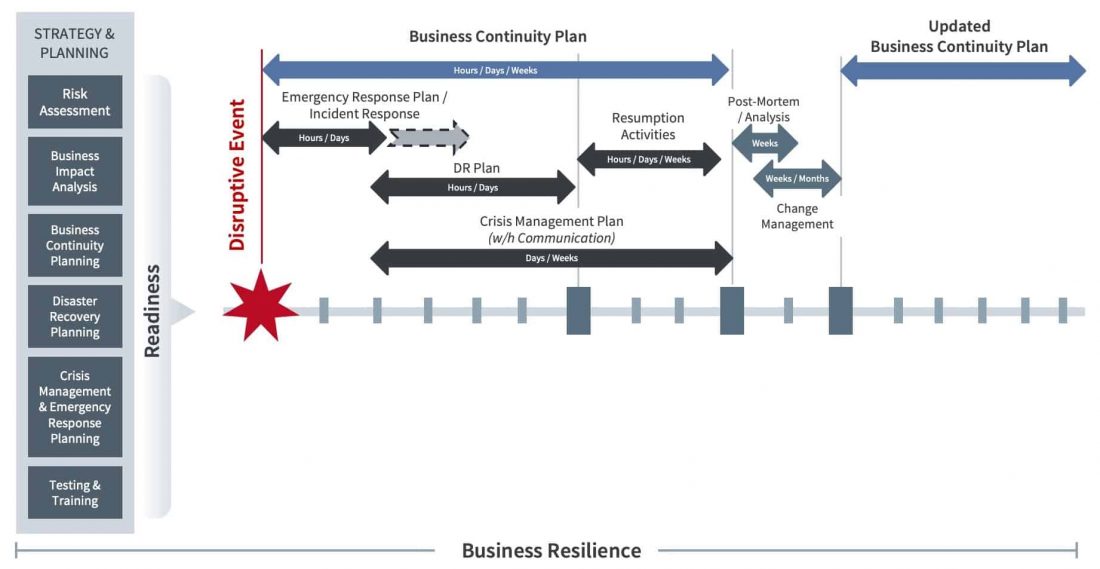
Figure 2: How business continuity supports business resilience
As shown in Figure 2, risk management for operational risks requires a business continuity plan and a disaster recovery plan, among other plans, to improve business resilience overall.
Comparing Resilience - 5-part miniseries
What is Business Resilience?
The Four Main Categories of Risks in Risk Management
Risk management covers strategic, financial, operational, and compliance and governance risks. Let's look at these four categories of business risk that organizations should address in the risk management process.
Strategic Risks
Strategic risks are internal and external risks that can prevent organizations from achieving their strategic objectives. These risks are caused by poor strategic decisions that negatively impacts the organization's long-term positioning and performance. This includes risks related to exploring new markets and expanding existing services. Some sources of strategic risks include the following:
- Reputational damage
- Unadopted technological innovations
- Financial issues as a result of cost pressures, cashflow or loss of capital
- HR issues
- Change management
- Evolving customer needs and preferences
- Market or industry changes
- Supply and value chain issues
Financial Risks
Financial risk impacts an organization's ability to fulfill its financial obligations, manage debt, and maintain sufficient cash flow needed for ongoing operations. Commodity price fluctuations, interest rates, foreign currency exchange rates, market movements, intense competition from similar businesses are all factors that contribute to financial risks.
The strategies for mitigating financial risks target limiting the amount or tenure of loans, diversifying income streams, resolving cash flow issues, and obtaining insurance.
Compliance and Governance Risks
Compliance and governance risks arise when organizations flagrantly or accidentally flout laws, regulatory requirements, and other legal benchmarks that guide business operations. Compliance risks can result from human error, lack of due diligence, insufficient control systems, and inadequate training.
In some cases, new laws or regulations (or modification of existing ones) can result in compliance risks. For instance, taxes, equipment certification, and occupational health and safety requirements are constantly changed or updated by governments and relevant authorities. Being unaware of these changes can lead to costly penalties, litigation, legal risks, and bad publicity (a precursor to reputational risk).
Operational Risks
Operational risks arise when inefficient policies, systems, and processes negatively impact an organization's day-to-day business operations. This risk exposes organizations to the risk of loss due to external events, human error, inefficient systems, and lack of proper procedures. Sources of operational risk are both internal and external:
- Employee errors
- Fraud activity and misuse of assets
- Technical failures
- Hacking, data theft, cyberattacks including ransomware
- Process management such as non-reporting, data entry, and accounting errors
- Business disruption due to IT system failures and utility downtime
- Damage to physical assets caused by vandalism, equipment maintenance, natural disasters
- Third-party vendor or partner failure, victim of a disruption, as a conduit for a cyberattack
- Workplace policies and safety
Zerto as a Risk Control Tool
One way to mitigate the risk of a significant disruption is to deliver speed and effectiveness over the recovery phase. This is an effective control used in risk management for operational risks.
Zerto, a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company, does just that. It ensures that IT systems remain resilient through planned and unplanned disruptions by delivering the RPOs and RTOs that meet the most stringent SLAs driven by your business continuity requirements.
Fast and effective Recovery with Zerto
Other Resources
LATEST FROM ZERTO SEE ALL
Business Resilience
Risk management aims at ensuring business continuity and ultimately helps to make a business resilient.
Essential Guide: Business Continuity
Gain a better understanding of what business continuity means and what it takes to achieve it.
Essential Guide: Disaster Recovery
Get everything you need to know about disaster recovery in one guide.
What is Zerto?
Learn about Zerto and how it can help you solve your data protection and recovery challenges.